KANYA PATIL-14021
In the
11th and 12th session of BA we learnt about what is
Multi-dimensions scaling. In this there are 2 methods.
a)
Overall
Similarity – The
main advantage of overall similarity method is that, it throws up latent
attribute that may not always be considered or known to us.
It
is where we present the respondents with different
pairs of objects and ask how similar or dissimilar the objects are.
The
disadvantage of overall similarity is that it needs complete knowledge to
interpret.
b)
Attribute
Based – The main
advantage of attribute based method is that, it is easy to execute. In this
method we ask people to rank attributes and map
them. The disadvantage is that there is a threat of missing important
attribute.
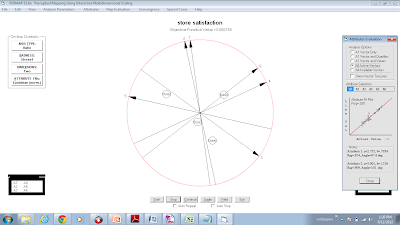
In today’s session, we mapped the variable ‘‘store satisfaction’’
for 4 stores based on 6 attributes. Quality satisfaction, price satisfaction, etc.
The proximity matrix looks like this:
Title- Store Satisfaction
nObjects - 4
nAttributes - 6
Attribute List
Store 1
3.01 3.08
3.25 3.18
3.17 2.99
Store 2
3.21 3.10
2.94 2.88
3.31 3.00
Store 3
3.16 3.09
3.23 3.30
3.08 3.31
Store 4
2.97 3.04
3.31 3.01
3.08 3.07
The
PERMAP looks like this.
We
also studied Distance Matrix, Similarity Matrix and Dissimilarity Matrix.
1)
Distance
Matrix: In mathematics, computer science and graph theory, a distance matrix is a matrix (two-dimensional
array) containing the distances, taken pairwise, of a set of points. This
matrix will have a size of N×N (where N is the number of
points, nodes or vertices
2)
Similarity
Matrix: In this, diagonals will always contain 1. For example, in mobile users
we saw that sms, alarm, time&date, games come together because of highest
number of yes matches, since we use binary variables and jaccard method.
3)
Dissimilarity
Matrix: In this, diagonals will always contain 0. For example, in distance
between cities, where we used Euclidean distance, the distance between a city
and itself will always be 0.
Permap Software:
PERMAP
is a free, Windows-based real-time interactive program for making perceptual
maps also called product maps, strategic maps, sociograms, sociometric maps,
psychometric maps, stimulus-response maps, relationship maps, concept maps, etc.
Its fundamental purpose is to uncover any "hidden structure" that
might be residing in a complex data set. PERMAP takes object-to-object
proximity values (similarities, dissimilarities, correlations, distances,
interactions, psychological distances, dependencies, confusabilities,
preferences, joint or conditional probabilities, etc.), or up to 30 object
attribute values, and uses multidimensional scaling (MDS) to make a map that
shows the relationships between the objects. Succinctly, it makes classical
metric and nonmetric MDS analyses in one, two, three, … or eight dimensions,
for one-mode two-way or two-mode two-way data, with up to 1000 objects and with
missing values allowed. In addition, it can make several new types of MDS
analyses involving error bounds or boundary conditions and it can show the
affect of degrading the similarity information.
No comments:
Post a Comment